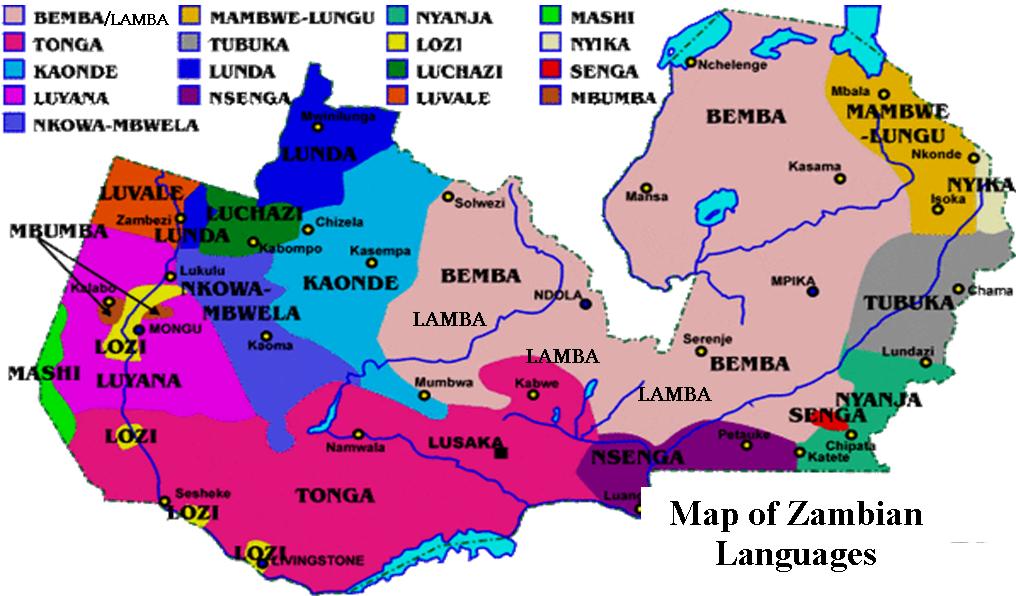
Zambian Languages
Zambia has several major indigenous languages, all of them members of the Bantu family, together with English, which is the official language and the major language of business and education.
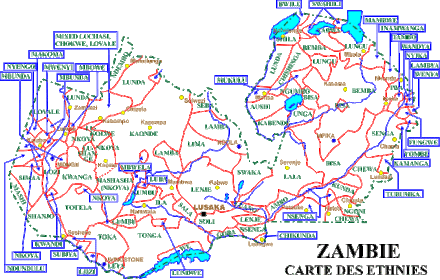
Zambia is widely claimed to have over 72 languages, although many of these might be better regarded as dialects. Some of these languages have a long history within Zambia, while others, such as Lozi, arose as a result of 18th and 19th-century migrations. All of Zambia's vernacular languages are members of the Bantu family and are closely related to one another.
The major indigenous Zambian languages spoken are: Bemba, Nyanja, Tonga, Lozi, Lunda, Kaonde and Luvale. In fact, about 90 percent of Zambians belong to these groups.
There are also other indigenous language groups such as Lamba, Ila, Mambwe, Namwanga, Tumbuka, Aushi, Lenje, Lala and so many others!
Just imagine, over 70 different languages have been identified in Zambia! One wouldn’t be faulted to think that because of this diversity of languages the country would be plunged into conflicts. But far from it! Strangely enough the country has been a haven of peace since independence in 1964!
Contributing to the peace which Zambia has enjoyed is the “One Zambia One Nation” slogan coined by the first Zambian president, Dr. Kenneth Kaunda .
Another contributing factor is the Zambian Official language, which happens to be English. With this selection, no particular tribe feels superior to others.
The coming together of different people from different tribal backgrounds to urban centers and the mines on the copperbelt has contributed to the developing of a gregarious and friendly atmosphere. This has led to people marrying across tribal lines, which was not common before.
Copperbelt Province Language
Lamba and Bemba are the main languages spoken in the Copperbelt province.
Lamba is a language found in Zambia and is commonly spoken in the Copperbelt. There are about 210,000 native speakers in the northern parts of Zambia and southern fringes of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Lamba is also spoken in Lusaka, mainly because many speakers have migrated there for jobs. Lamba is a Bantu language. (In fact, "mu ntu" means "one person" in Lamba and "ba ntu" means "two or more people".) Since the two languages (Bemba and Lamba) share many words, some people might say Lamba is a dialect of Bemba.
Lambaland stretches on both sides of Zambia and Congo. It stretches from Ndola to Solwezi; from Ndola to Serenje? from Ndola through Mpongwe, Chief Ngabwe to Chief Mulendema in Mumbwa. Even the Ila tribe across this area still speak Lamba to date though their present generation cannot still explain why. (Contributed by: Carlson Chingwengwezi).
Lusaka Province Language
Nyanja, commonly called Ici Nyanja, is spoken in the capital city of Lusaka. The same language is also known as Ichi Chewa in Eastern province.
It is worth noting here that all languages are spoken in almost all provinces, but they are specifically prominent in certain areas…. However, Bemba is now getting an upper-hand!
And the following are Zambian languages spoken in different provinces...
Zambian Languages By Province
North Western Province
- Lunda - Luvale
- Luchazi
- Kaonde
- Toka - Leya
- Tonga
- Baila
- Lamba
- Bemba
- Bisa
- Swaka
- Lala
- Lamba
- Lozi
- Aushi
- Bemba
- Lungu
- Namwanga
- Mambwe
- Nyika
- Bisa
- Chewa
- Kunda
- Ngoni
- Tumbuka
- Nsenga
- Nsenga Luzi
- Cikunda
- Nyanja
- Lenje
- Soli